Fungi are a cannabis grower’s absolute nightmare. Annoying guests that generally appear in autumn and during the rainy season, determined to ruin the whole crop. There are indeed several preventive measures to avoid the conditions that provoke the appearance of these pathogens (limited ventilation, heat, humidity…). In this post we explain which are the most common fungi that could attack your marijuana plants, how to prevent them and, in case that they’ve already settled in, how to fight them.

Indice
Some of the fungi that can attack your cannabis crop are Botrytis, Powdery Mildew, Damping off, Mildew, Alternaria, and Fusarium. In this post we explain how to identify and fight these so that they don't ruin your crop. We'll start by explaining how to prevent them, as one of the keys to cannabis growing is prevention, and in this case the prevention methods are identical for all of them. Here you'll find a series of measures that should be taken to prevent the appearance of any type of fungus.

How to protect your cannabis crop from fungi
- Hygiene: keeping your crop clean is paramount to avoid the appearance of fungi. Whether you're growing indoors or outdoors, you have to constantly clean the area and remove dead leaves because rotten matter can be a source of infection. Disinfect all the utensils you use thoroughly. If cultivating indoors, give the whole area a proper cleanup between each crop.
- Temperature and humidity control: indoors, try to keep the room well aerated; the relative humidity should be lower than 50 %, and the temperature below 77ºF. If you're growing outdoors and live in a rather humid region, it is best you choose fast-flowering strains.
- Preventive products: there are quite a lot of organic fungicides that can help prevent the appearance of fungi.
However, despite taking all these preventive measures, these tiny organisms sometimes seem to find a way onto our beloved plants and end up colonizing them. Below you'll find some of the most common fungi that can attack your marijuana plants, as well as some tips on how to identify and combat them.
Botrytis

What is Botrytis?
This pathogenic fungus is easy to recognize because it creates a necrosis process that affects all plant tissue (including leaves, buds, stalks, etc). This gives the plants a dry and lifeless appearance. It is one of the worst types of fungus since it spreads very quickly and we need to act very fast if we want to stop it from destroying the whole crop.
How to fight Botrytis
- Prevention: monitor moisture levels.
- If the fungus has already settled in, cut off the infected parts, also taking off some centimeters of the healthy tissue.
- Get rid of those infected parts and disinfect the utensils you've used.
- Improve ventilation.
- Raise the temperature to 78ºF and reduce relative humidity to below 50%.
- If your plants have already reached the last phase of the flowering, harvest ASAP.
Powdery Mildew
What is Powdery Mildew?
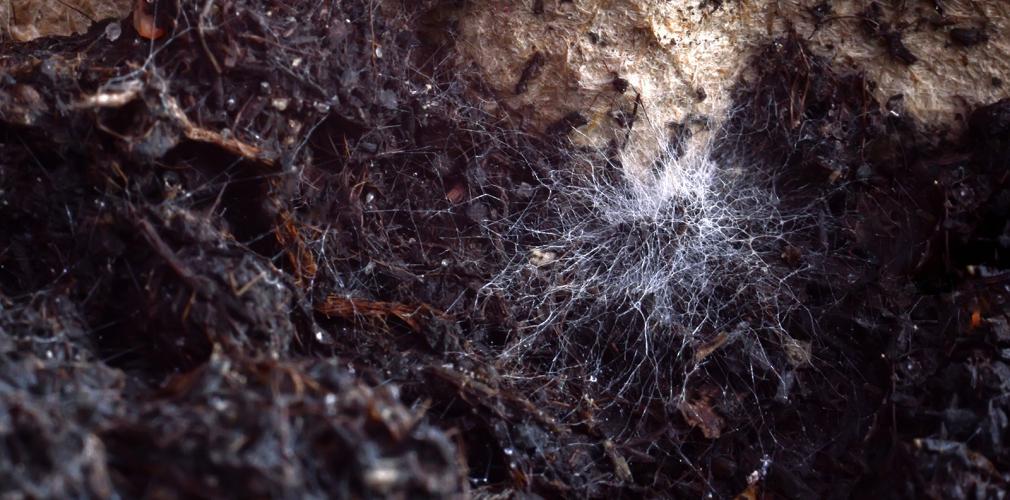
Powdery mildew is one of the most common fungi in cannabis plants. It is also rather easy to identify because a thin layer of white dust appears on the top part of the leaves. At the beginning you'll see some small circles of dust that little by little spread and become denser.

How to fight powdery mildew
Removing all trace of powdery mildew as soon as it becomes visible is crucial. Otherwise, if the fungus finds its way into the bud, the whole crop will be ruined because the flowers won't be fit for consumption.
Preventive products: in order to prevent the appearance of this fungus, you can use organic products such as horsetail and propolis. You can also use an antagonistic fungus called Trichoderma harzianum, which is to be injected in the substrate we're going to use for growing our cannabis plants. However, if powdery mildew has already settled on your plants…
- Spray water with high levels of pH (8- 8.5). Reapply every 3-4 days.
Spray a water/milk solution (90% water and 10% milk).
Spray a mix of water with a squirt of hydrogen peroxide.
Damping off
What is Damping off?
This disease can be caused by several types of fungi, both seed-borne and soil-borne. It is basically a rotting process that affects seeds and seedlings. This process starts when the environmental conditions are not adequate, particularly due to high humidity levels and poor ventilation. Damping off is very easy to identify because it tends to decompose the lowest part of the stem until the seedling is unable to support itself and dies. Everything happens very fast, usually overnight.
How to fight Damping off
There is nothing we can do once it hits the plants because, as mentioned earlier, it progresses rapidly and is lethal; and, above all, it attacks plants in their first stage of life, when they're at their most vulnerable. However, what we can and MUST do as soon as possible is remove all infected seedlings to prevent the disease from spreading. We can also prevent its appearance by applying Pythium oligandrum (a parasite that feeds on certain fungi) as well as by using a sterile substrate.
Mildew

What is Mildew?
Unlike other fungi, mildew grows inside the plant's tissue, such as its leaves and stems, and therefore is only visible during advanced stages of growth. The earliest sign of mildew is the appearance of whitish and yellowish spots on the leaves. These 'oil stains' are more yellowy on the top side of the leaf, whereas they exhibit more greyish tones on the underside. Once plants have been infected, they lose their vigour, their growth slows down, and their leaves become yellow and eventually fall off.
How to fight mildew
Once we can see clear signs that our cannabis plants have been infected with mildew, it is paramount to eliminate the damaged areas or even entire plants, depending on the level of infection, so as to make sure that healthy plants do not become infected. It is also advisable to add fungicides to the nutrient solution and to spray a water and fungicide solution all over the affected areas.
Alternaria
What is Alternaria?

Alternaria (or Alternaria alternate) has been identified as one of the most common fungi to attack cannabis plants. It is part of a group of fungi (Pleosporaceae) that includes 44 different species spread virtually all around the world, and is closely linked to the decomposition of organic matter. Some of them cause other diseases too, such as root rotting, and can directly propagate through the tissue of infected plants. They reproduce rapidly and can become a huge problem for large-scale cannabis crops, small plantations, or even individual plants.
How to fight Alternaria?
Alternaria can be really dangerous for your crop if not detected and treated appropriately, so the most effective course of action is always prevention. An infected cannabis plant has little chance of surviving, even when spraying it with fungicides. Therefore, the wisest decision is to get rid of the whole plant straightaway. This may be disappointing, but at least you'll know there's no risk of this fungus spreading to other plants.
Fusarium
What is Fusarium?

Fusarium is almost certainly the most aggressive fungus that there is. Once it manages to settle on a crop, the plants will more than likely end up dying. Fusarium can attack the plants in different ways: some strains parasitize the radicular system, whilst others attack their vascular system. Fusarium symptoms are clearly visible, especially as this fungus acts quickly, making the plant dry out either partially or completely, making it look as if it were in need of water.
How to fight Fusarium?
Unfortunately, plants that have been infected by Fusarium will most likely end up dying because there are currently no 100% effective treatments for this fungus on the market. Therefore, prevention is always the best plan of action. Another option is to look for natural allies like mycorrhiza, a beneficial fungus that makes plants stronger by working as a shield against the attack of fungi on the roots.
Pythium
What is Pythium?
Pythium is a false fungus. It is one of the most dangerous parasites and causes the largest number of deaths during the first days of growing. It is common to find seedlings at very early stages of life that already show a bent stem due to Pythium. Pythium refers to a genus of parasitic oomycotes, usually parasites in seaweed or small aquatic animals in their simplest form, as well as in more complex terrestrial plants. Therefore these organisms can live in both the irrigation water and in the soil. They often appear in greenhouses and can spread rapidly if the conditions are right.
How to combat Pythium?
Using a sterile substrate is the best way to prevent the appearance of Pythium. Mycorrhizae can also be applied, and avoiding the formation of puddles or excess moisture in the soil is also recommended.










Give us your feedback
Your rating (between 1 and 5)
1 2 3 4 5Leave a comment